# vue相关的面试题
# 1. 谈一下你对MVVM原理的理解
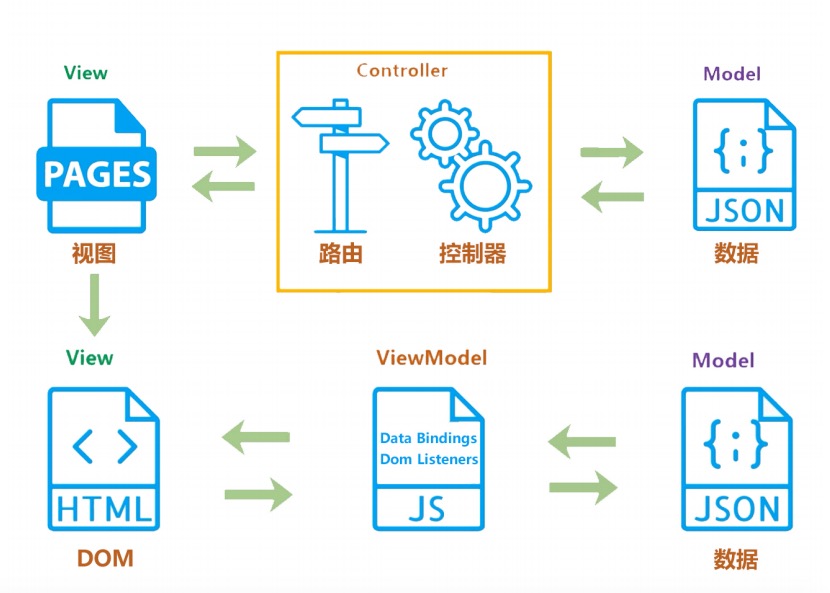
说起MVVM, 那么就要说下以前的MVC模式,MVC模式,指的是用户在界面操作时,会请求服务器路由,路由会调用对应的控制器来处理,控制器会拿到数据之后,再返回给前端,页面重新渲染
MVVM: 传统的前端会通过操作dom,将数据渲染在页面上, 但MVVM不同, v就是视图,M就是数据,而VM, 就是vue内部帮我们实现了数据渲染操作,通过数据来驱动视图, 当数据有更新变化的时候,vue会自动的通知视图层更新数据(双向数据绑定)
# 2. 请说一下响应式数据的原理?
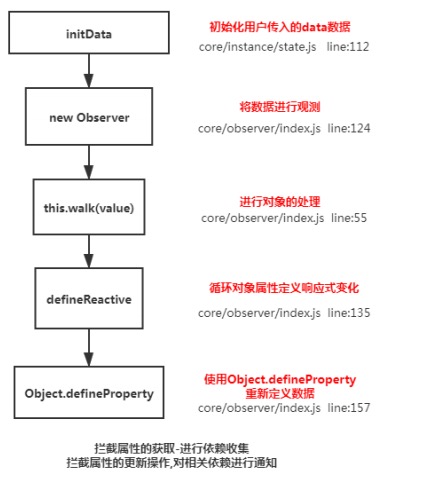
vue是通过Object.defineProperty,数据劫持来实现响应式数据的。当vue初始化数据的时候,会将data里面的数据通过setter, getter, 来劫持数据,
当对应属性,进行依赖收集到当前组件的watcher(渲染类型watcher), 当数据发生变化的时候,会通过watcher通知相关依赖进行更新。
// core/observer/index defineReactive方法中
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get: function reactiveGetter () {
const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val
if (Dep.target) {
dep.depend() /* 收集依赖 */
if (childOb) {
childOb.dep.depend()
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
dependArray(value)
}
}
}
return value
},
set: function reactiveSetter (newVal) {
const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val
if (newVal === value || (newVal !== newVal && value !== value)) {
return
}
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && customSetter) {
customSetter()
}
if (getter && !setter) return
if (setter) {
setter.call(obj, newVal)
} else {
val = newVal
}
childOb = !shallow && observe(newVal)
dep.notify() /**通知相关依赖进行更新**/
}
})
# 3.Vue中是如何检测数组变化?
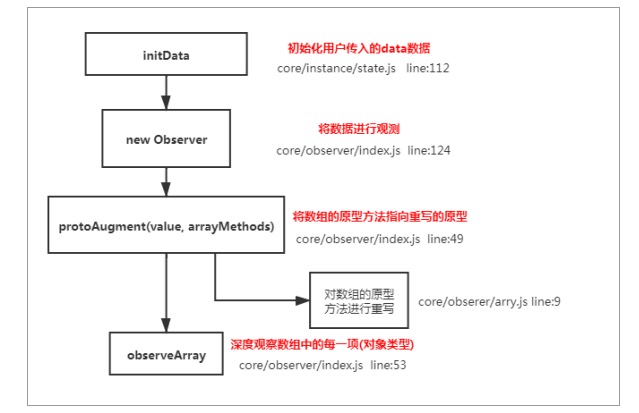
- Vue是采用函数劫持的方式,来重写数组方法的
- Vue将data中的数组,通过原型链来重写,指向自己自定义的数组原型方法。当调用数组的api时,会调用自己定义的方法,从而检测数组变化
// core/observer/array
const arrayProto = Array.prototype
export const arrayMethods = Object.create(arrayProto)
const methodsToPatch = [
'push',
'pop',
'shift',
'unshift',
'splice',
'sort',
'reverse'
]
/**
* Intercept mutating methods and emit events
*/
methodsToPatch.forEach(function (method) { // 重写原型方法
// cache original method
const original = arrayProto[method] // 调用原数组的方法
def(arrayMethods, method, function mutator (...args) {
const result = original.apply(this, args)
const ob = this.__ob__
let inserted
switch (method) {
case 'push':
case 'unshift':
inserted = args
break
case 'splice':
inserted = args.slice(2)
break
}
if (inserted) ob.observeArray(inserted)
// notify change
ob.dep.notify() // 当调用数组方法后,手动通知视图更新
return result
})
})
# 4.为何Vue采用异步渲染?
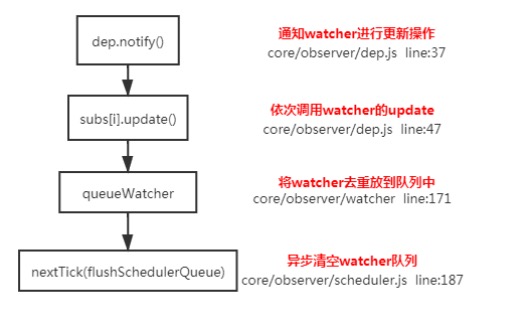
理解:因为如果不采用异步更新,那么每次更新数据都会对当前组件进行重新渲染.所以为了性能考虑。 Vue 会在本轮数据更新后,再去异步更新视图!
// core/observer/watcher
update () {
/* istanbul ignore else */
if (this.lazy) {
this.dirty = true
} else if (this.sync) {
this.run()
} else {
queueWatcher(this)
}
}
// core/observer/scheduler
export function queueWatcher (watcher: Watcher) {
const id = watcher.id
if (has[id] == null) {
has[id] = true
if (!flushing) {
queue.push(watcher)
} else {
// if already flushing, splice the watcher based on its id
// if already past its id, it will be run next immediately.
let i = queue.length - 1
while (i > index && queue[i].id > watcher.id) {
i--
}
queue.splice(i + 1, 0, watcher)
}
// queue the flush
if (!waiting) {
waiting = true
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && !config.async) {
flushSchedulerQueue()
return
}
nextTick(flushSchedulerQueue)
}
}
}
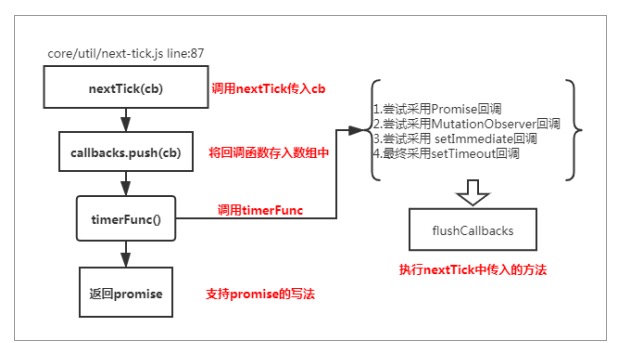
# 5.nextTick实现原理?
nextTick主要采用的是宏任务和微任务,通过定义一个异步方法,当多次调用nextTick的时候,会将回调函数通过数组的形式插入到队列中
// core/util/next-ticks
// 定义个异步方法
let timerFunc
if (typeof Promise !== 'undefined' && isNative(Promise)) {
const p = Promise.resolve()
timerFunc = () => {
p.then(flushCallbacks)
if (isIOS) setTimeout(noop)
}
} else if (!isIE && typeof MutationObserver !== 'undefined' && (
isNative(MutationObserver) ||
// PhantomJS and iOS 7.x
MutationObserver.toString() === '[object MutationObserverConstructor]'
)) {
// Use MutationObserver where native Promise is not available,
// e.g. PhantomJS, iOS7, Android 4.4
// (#6466 MutationObserver is unreliable in IE11)
let counter = 1
const observer = new MutationObserver(flushCallbacks)
const textNode = document.createTextNode(String(counter))
observer.observe(textNode, {
characterData: true
})
timerFunc = () => {
counter = (counter + 1) % 2
textNode.data = String(counter)
}
} else if (typeof setImmediate !== 'undefined' && isNative(setImmediate)) {
// Fallback to setImmediate.
// Techinically it leverages the (macro) task queue,
// but it is still a better choice than setTimeout.
timerFunc = () => {
setImmediate(flushCallbacks)
}
} else {
// Fallback to setTimeout.
timerFunc = () => {
setTimeout(flushCallbacks, 0)
}
}
// nextTick实现
export function nextTick (cb?: Function, ctx?: Object) {
let _resolve
callbacks.push(() => {
if (cb) {
try {
cb.call(ctx)
} catch (e) {
handleError(e, ctx, 'nextTick')
}
} else if (_resolve) {
_resolve(ctx)
}
})
if (!pending) {
pending = true
timerFunc() // 执行异步方法
}
// $flow-disable-line
if (!cb && typeof Promise !== 'undefined') {
return new Promise(resolve => {
_resolve = resolve
})
}
}
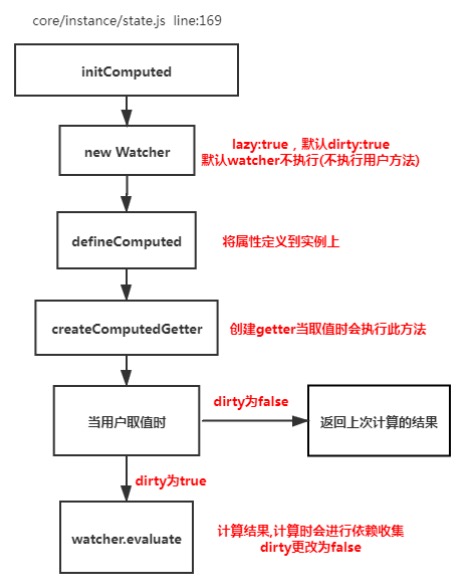
# 6. Vue中Computed的特点
Computed也是一个watcher,但他具有缓存,只有依赖的属性发生变化的时候,才会更新视图
// core/instance/state
function initComputed (vm: Component, computed: Object) {
// $flow-disable-line
const watchers = vm._computedWatchers = Object.create(null)
// computed properties are just getters during SSR
const isSSR = isServerRendering()
for (const key in computed) {
const userDef = computed[key]
const getter = typeof userDef === 'function' ? userDef : userDef.get
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && getter == null) {
warn(
`Getter is missing for computed property "${key}".`,
vm
)
}
if (!isSSR) {
// create internal watcher for the computed property.
watchers[key] = new Watcher(
vm,
getter || noop,
noop,
computedWatcherOptions
)
}
// component-defined computed properties are already defined on the
// component prototype. We only need to define computed properties defined
// at instantiation here.
if (!(key in vm)) {
defineComputed(vm, key, userDef)
} else if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
if (key in vm.$data) {
warn(`The computed property "${key}" is already defined in data.`, vm)
} else if (vm.$options.props && key in vm.$options.props) {
warn(`The computed property "${key}" is already defined as a prop.`, vm)
}
}
}
}
function createComputedGetter (key) {
return function computedGetter () {
const watcher = this._computedWatchers && this._computedWatchers[key]
if (watcher) {
if (watcher.dirty) { // 如果依赖的值没发生变化,就不会重新求值
watcher.evaluate()
}
if (Dep.target) {
watcher.depend()
}
return watcher.value
}
}
}
# 7.Watch中的deep:true 是如何实现的
当用户指定了 watch 中的deep属性为 true 时,如果当前监控的值是对象类型。会对对象中的每一项进行求值,此时会将当前 watcher 存入到对应属性的依赖中,这样数组中对象发生变化时也会通知数据更新
// core/observer/watcher
get () {
pushTarget(this)
let value
const vm = this.vm
try {
value = this.getter.call(vm, vm)
} catch (e) {
if (this.user) {
handleError(e, vm, `getter for watcher "${this.expression}"`)
} else {
throw e
}
} finally {
// "touch" every property so they are all tracked as
// dependencies for deep watching
if (this.deep) {
traverse(value)
}
popTarget()
this.cleanupDeps()
}
return value
}
core/observer/traverse
function _traverse (val: any, seen: SimpleSet) {
let i, keys
const isA = Array.isArray(val)
if ((!isA && !isObject(val)) || Object.isFrozen(val) || val instanceof VNode) {
return
}
if (val.__ob__) {
const depId = val.__ob__.dep.id
if (seen.has(depId)) {
return
}
seen.add(depId)
}
if (isA) {
i = val.length
while (i--) _traverse(val[i], seen)
} else {
keys = Object.keys(val)
i = keys.length
while (i--) _traverse(val[keys[i]], seen)
}
}
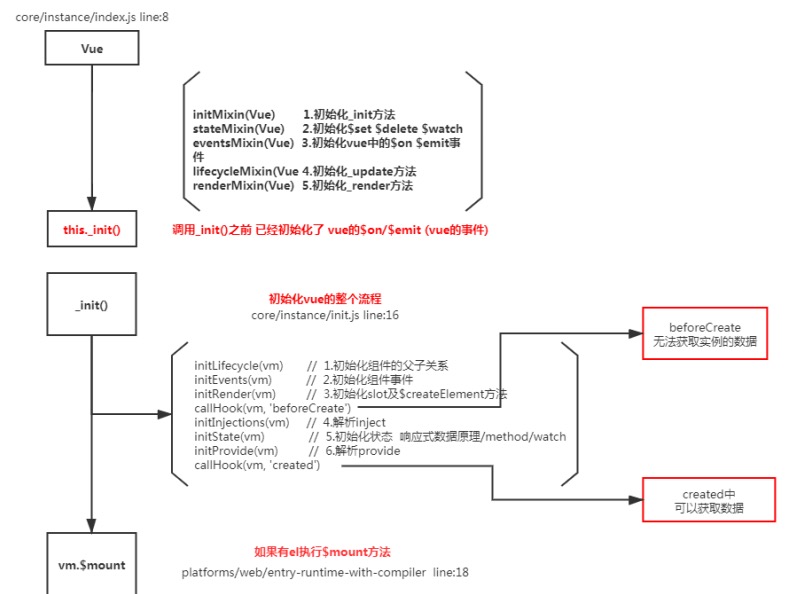
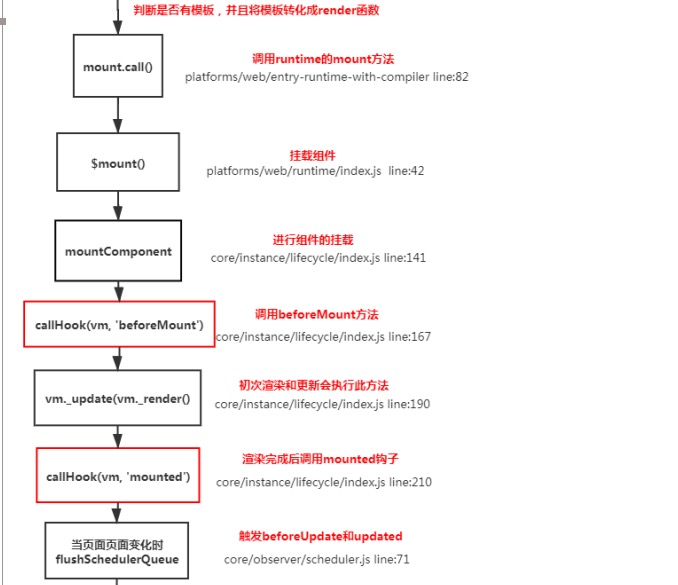
# 8.Vue组件的生命周期
beforeCreate在实例初始化之后,数据观测(data observer) 之前被调用created实例已经创建完成之后被调用。在这一步,实例已完成以下的配置:
数据观测(data observer),属性和方法的运算, watch/event 事件回调。这里没有$el
beforeMount在挂载开始之前被调用:相关的 render 函数首次被调用mountedel 被新创建的 vm.$el 替换,并挂载到实例上去之后调用该钩子beforeUpdate数据更新时调用,发生在虚拟 DOM 重新渲染和打补丁之前updated由于数据更改导致的虚拟 DOM 重新渲染和打补丁,在这之后会调用该钩子beforeDestroy实例销毁之前调用。在这一步,实例仍然完全可用destroyed实例销毁后调用。调用后, Vue 实例指示的所有东西都会解绑定,所有的事件 监听器会被移除,所有的子实例也会被销毁。 该钩子在服务器端渲染期间不被调用
要掌握每个生命周期内部可以做什么事
created实例已经创建完成,因为它是最早触发的原因可以进行一些数据,资源的请求mounted实例已经挂载完成,可以进行一些DOM操作beforeUpdate可以在这个钩子中进一步地更改状态,这不会触发附加的重渲染过程。updated可以执行依赖于 DOM 的操作。然而在大多数情况下,你应该避免在此期间更改状态,因为这可能会导致更新无限循环。 该钩子在服务器端渲染期间不被调用。destroyed可以执行一些优化操作,清空定时器,解除绑定事件

# 9.v-for与v-if为何不能连用
v-for优先于v-if, 如果连用的话,那么v-for先执行,之后再判断v-if,这样性能这块非常的低 所以一般用v-if放入外层的template
# 10.diff算法的时间复杂度
两个树的完全的 diff 算法是一个时间复杂度为 O(n3) , Vue 进行了优化·O(n3) 复杂度的问题转换成 O(n) 复杂度的问题(只比较同级不考虑跨级问题) 在前端当中, 你很少会跨越层级地移动Dom元素。 所 以 Virtual Dom只会对同一个层级的元素进行对比。
# 11.简述Vue中diff算法原理
1.先同级比较,在比较子节点
2.先判断一方有子节点一方没子节点的情况
3.比较都有子节点的情况, 递归比较子节点
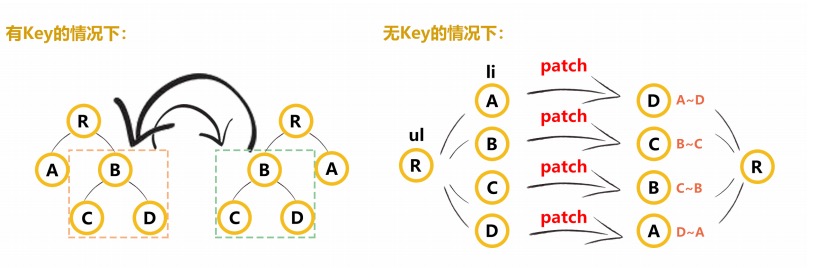
# 12.v-for中为什么要使用key
key是需要唯一标识,而且是不可变的,防止后续修改删除列表的时候造成bug vue对通过diff算法,复用原则,判断两个dom节点是否一样,如果一样的话会复用原来的dom节点 key不能是index,不然也会有同样问题。
如果静态列表的话,就没有删除修改操作,也就index是唯一标识,就不会有问题
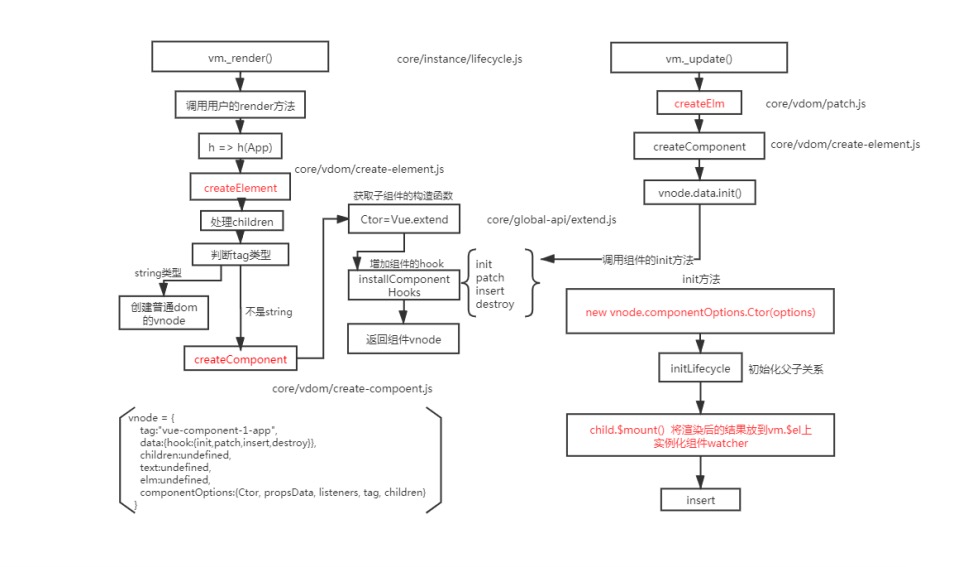
# 13. 描述组件渲染和更新过程
组件渲染的时候,通过render函数生成虚拟节点,再调用vue.extends方法来构建子组件的构造函数,并且实例化,最后调用$mount()方法挂载在页面上。
更新的时候,使用的是diff算法比对节点
# 14. 组件中的 data为什么是一个函数?,为什么new Vue的data可以放对象
避免同一组件,创建多次实例,而实例使用的同一个构造函数,实例的数据互相影响,保持数据的独立性
什么时候用new Vue,这个是在main.js,根组件实例的时候就一样,我们写项目的时候就只有一个实例
# 15.vue中事件绑定的原理
- 原生dom的事件绑定, 原生事件
- 组件的自定义事件
# 16.v-model中的实现原理及如何自定义v-model
- 原生的 v-model ,会根据标签的不同生成不同的事件和属性
- 组件的v-model 就是value+input的语法糖
自定义v-model
Vue.component('el-checkbox',{
template:`<input type="checkbox" :checked="check"
@change="$emit('change',$event.target.checked)">`,
model:{
prop:'check', // 更改默认的value的名字
event:'change' // 更改默认的input方法名
},
props: { check: Boolean }
})
# 17.Vue中v-html会导致哪些问题
- 可能会导致 xss 攻击
- v-html 会替换掉标签内部的子元素
- 样式需要通过deep来添加scoped
# 18.Vue父子组件生命周期调用顺序
组件的调用顺序都是先父后子,渲染完成的顺序肯定是先子后父
组件的销毁时是先父后子,销毁完成的顺序是先子后父
同步
加载渲染过程
父beforeCreate->父created->父beforeMount->子beforeCreate->子created->子beforeMount- >子mounted->父mounted
异步
父beforeCreate->父created->父beforeMount->父mounted->子beforeCreate->子created->子beforeMount- >子mounted
子组件更新过程
父beforeUpdate->子beforeUpdate->子updated->父updated
父组件更新过程
父beforeUpdate->父updated
销毁过程
父beforeDestroy->子beforeDestroy->子destroyed->父destroyed
# 19.Vue组件如何通信? 单向数据流
- 父子间通信 父->子通过
props、子-> 父$on、$emit(发布订阅) - 获取父子组件实例的方式
$parent、$children - 在父组件中提供数据子组件进行消费
Provide、inject插件 Ref获取实例的方式调用组件的属性或者方法(如果给dom写,获取dom元素,如果给组件写,就获取组件的实例)Event Bus实现跨组件通信 Vue.prototype.$bus = new Vue(公共的实例)Vuex状态管理实现通信 $attrs $listeners
# 20. Vue中相同逻辑如何抽离?
Vue.mixin 用法 给组件每个生命周期,函数等都混入一些公共逻辑
mixin使用的时候,找不到根源,就是看实例的时候就莫名多个数据
# 21.为什么要使用异步组件?
如果组件功能多,打包容量会特别大,需要采用异步组件,主要依赖于import()语法,可以实现文件按需加载
组件的定义,变成函数
# 22.什么是作用域插槽
插槽
// 子组件
<app><div slot="a">xxxx</div><div slot="b">xxxx</div></app>
// 父组件
slot name="a" slot name="b"
创建组件虚拟节点时候,遇到插槽slot属性,进行分类 渲染组件时,拿对应的slot属性的节点进行替换操作(插槽的作用域为父组件)
替换的过程,将父组件设置插槽的节点,设置到对应子组件的插槽里
作用域插槽(作用域在子组件) 子组件的数据,提供给父组件调用
初始化的时候不会渲染slot的子节点,用一个函数存起来 当调用的时候,才执行这个函数
# 23.谈谈你对 keep-alive 的了解?
keep-alive 可以实现组件的缓存作用 2个属性 include / exclude 2个生命周期 activated , deactivated
keep-alive是取第一个组件
用了rlu方法,当超出缓存最长个数时,会将最早缓存删掉
# 24. Vue中常见性能优化
- 编码优化
- 不要将所有的数据都放在data中,可以放在computed, 定时器可以不放data
- vue 在 v-for 时给每项元素绑定事件需要用事件代理
- SPA 页面采用keep-alive缓存组件
- 拆分组件( 提高复用性、增加代码的可维护性,减少不必要的渲染)
- key 保证唯一性
- 合理使用路由懒加载、异步组件
- 数据持久化的问题 (防抖、节流)
- 合理使用v-if和v-show
- Object.freeze 冻结数据
- 尽量采用runtime运行时版本
- Vue 加载性能优化:
- 图片懒加载 (https://github.com/hilongjw/vue-lazyload.git)
- 第三方模块按需导入 (babel-plugin-component)
- 滚动到可视区域动态加载 (https://tangbc.github.io/vue-virtual-scroll-list)
- 用户体验
- app-skeleton 骨架屏
- app-shell app壳
- pwa serviceworker
- SEO 优化:
- 预渲染插件 prerender-spa-plugin
- 服务端渲染 ssr
- 打包优化:
- 使用 cdn 的方式加载第三方模块
- 多线程打包 happypack
- splitChunks 抽离公共文件
- sourceMap 生成
- 缓存,压缩
- 客户端缓存、服务端缓存
- 服务端 gzip 压缩
# 25. Vue3.0你知道有哪些改进?
- Vue3 采用了TS来编写
- 支持 Composition API, 解决代码的条理性,mixins混乱问题,
- Vue3 中响应式数据原理改成 proxy
- vdom 的对比算法更新,只更新 vdom 的绑定了动态数据的部分
# 26. 实现hash路由和history路由
- onhashchange #
- history.pushState h5 api, 页面不存在的问题,所以通过服务端可以解决
(bilibili vue面试题)[https://www.bilibili.com/video/av90955610?from=search&seid=4442674282775134142]
